Pasadena Based African-American owned Cannabis Brand ‘Octavius – Masters of Buds’ Expands into Southern California through Collaboration with Sweet Flower
Octavius is committed to breaking through cannabis cliques and welcoming members of all walks of life to the global community of cannabis users and enthusiasts....
South Africa struggles with increased power cuts during electricity crisis
South Africans are struggling to cope with increased power cuts that have hit households and businesses across the country.
The post South Africa struggles with increased power cuts during electricity crisis appeared first on Digital Journal.
Raleigh NC Mold Testing and Remediation Boasts as The Go-To Mold Removal Company
Raleigh NC Mold Testing and Remediation is a top-rated mold treatment company. In a recent update, the agency outlined why it is the go-to company...
Why System Of Records (SOR) is critical for Prepaid Card Issuers?
Wallet limit breaches and data duplications are crucial problems for prepaid card issuers. They hold the risk of consumers overriding the loading and spending limit.
That’s why RBI mandated that all prepaid programs deploy a centralized System of Records (SOR) in October’17. All prepaid program partners must mandatorily connect to the issuer’s SOR system.
What is a System of Record?
A System Of Record (SOR) or Source System of Record (SSoR) is a single source of truth or data source that stores important information about a system or process within the organization. It serves as a shared reference point that protects prepaid card issuers against data repetitions that arise when individual data is created, handled, and processed by multiple individuals or business units. As a result, SOR provides a single source of truth for operations.
The System of Records monitors the consolidated prepaid balance of all wallets issued to the end customer by the same issuer, independent of the prepaid program partner. It is a central ledger that tracks every registered customer’s overall balance in real-time based on their KYC status. In addition to holding centralized data on the consolidated balance of a customer’s prepaid wallet, it also carries issuer-specific information. This is in cases where the balance of multiple partner wallets is integrated under a single PPI issuer.
How SOR works for prepaid cards?
Say an individual holds two prepaid wallets with the same issuer. His personal information is captured in the issuer database for profile creation and KYC verification. Issuers who partner with Token Service Providers for SOR will have all data automatically transferred to a centralized database. Then KYC-based wallet limit, dedupe check, and customer profile creation will need to be managed.
Why SOR is critical?
SOR is critical for prepaid issuers who deal with huge volumes of data from multiple source systems. This system of truth helps secure the integrity and validity of any data set as it remains the only source of truth. If there is any other agreed system of record, the data element must be either linked to or extracted from it. In other situations, the provenance and estimated data quality should be documented. Here are some key benefits SOR offers to users.
- Provides the most complete, accurate, and timely data
- Best structural conformance to the data model
- Nearest to the point of operational entry
- Can be used to feed other systems
How can M2P facilitate SOR implementation?
We help banks and prepaid card issuers build a SOR, which will serve as a final source of truth for all customer data. Our robust API-led infrastructure offers a centralized database to track and monitor the data in real-time. The built-in checks and balances comprise AML, negative listing, and real-time watch listing capabilities to ensure compliance and zero limit breaches across programs.
Looking to implement SOR for prepaid cards?
We would like to help. Write to us at [email protected].
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the latest fintech news, views, and insights, directly to your inbox.
Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for insightful fintech tales curated for curious minds like you.
Why System Of Records (SOR) is critical for Prepaid Card Issuers? was originally published in M2P Fintech on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Why Payments Interoperability is a Must for Today’s Generation?
Imagine you own a digital wallet. Its primary function is to let you spend viz., shop with partner merchants, make payments, and transfer money to other wallets and bank accounts. Then the same wallet offers a card (any authorized card network Visa, Mastercard, RuPay) to facilitate card-based in-store and online payments. Further, the wallet also comes with a UPI virtual ID to allow payments via QR codes and UPI.
This is payments interoperability making life easy for you.
What is Payments Interoperability?
Now, there are several definitions for interoperability. But at its core, it is the basic ability of multiple digital systems, applications, and databases to connect and communicate with each other.
Payment platforms leverage financial technology to connect and share data among ecosystem partners, viz., banks, payment gateways, payment processors, merchants, and consumers. This integration helps carry out transactions between payment service providers, third-party processors, and other networks without hassles. The interoperability occurs at the origination point, at the network level, or through an intermediary, both in national and international payment systems.
Here are a few common attributes of interoperability.
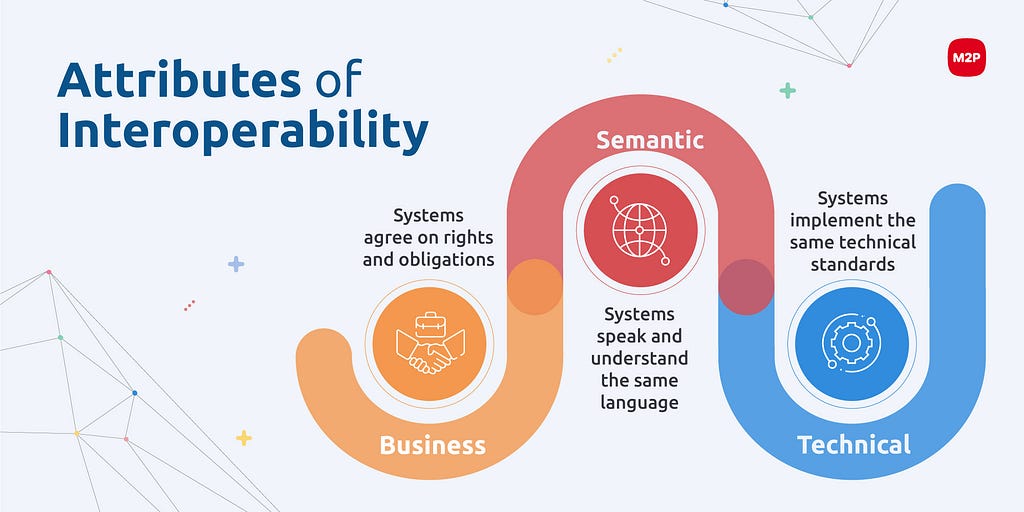
Payment system interoperability can be at domestic (national) and international levels.
National Payments Interoperability
National payment interoperability is limited to payment systems within a single country. National interoperability usually involves the same type of accounts. It happens between:
- Deposit accounts issued by various banks
- e-money transaction accounts offered by mobile network operators
National interoperability is ensured through bilateral agreements between Payment Service Providers (PSP) and Payment Systems Infrastructures (PSIs). Or through a centralized interoperability solution, with standardized regulatory measures stipulated by the central bank.
RBI’s Mandate for Domestic PPI Interoperability
Governments and Central Banks are giving interoperability a significant push to accelerate cashless ecosystems. RBI aims to make interoperability mandatory for all full-KYC Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) and acceptance infrastructure by 31 June 2022. The move is to drive inclusion in cashless payments, and optimally utilize payment instruments like cards and wallets, given the constraint of scarce acceptance infrastructures like point-of-sale (POS) devices, ATMs, QR codes, and bill-payment touch points. Any user who signs up for a wallet, payment card, or UPI on PPI rails should be able to make digital payments via any network.
LivQuik is the first PPI issuer in India to achieve full interoperability as mandated by the RBI. This feat enables customers to enjoy optimized card and UPI payments across wallets. Similarly, initiatives like Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) will further drive interoperability, inclusion, and innovation.
Need for Interoperable Cross-Border Payments
Interoperability in cross-border payments is critical to making financial services accessible, affordable, and reliable. It involves coordination between multiple stakeholders, including central banks and regulators. It encompasses technical, regulatory, and usage interoperability to enable quick, convenient, secure, and seamless transactions regardless of the Financial Services Provider (FSP) network.
According to a recent Visa survey, only 50% of merchants have a cross-border trade-compatible payment processing infrastructure. Without globally interoperable payment systems, small and medium-sized merchants cannot tap into international trade and markets. Interoperability levels the playing field and eliminates the inefficiencies of a closed-loop payment systems, i.e., payments between users of only one payment provider.
An end-to-end interoperable platform delivers access to cross-border payment services through an integrated gateway. It enhances the user experience through its ease-of-use customer onboarding and digital KYC.
A centralized interoperability platform calls for stringent global regulatory compliance and data security standards for utmost security. It enables faster reconciliations with real-time reporting and data-driven insights into payment patterns and customer behavior. Moreover, an automated platform saves time, reduces human error, and cuts costs. It enables infrastructure and data sharing which helps tech-driven payment ecosystems reach economies of scale.
While international interoperability comes with a few challenges, it can be overcome with the support of the regulators, the global schemes, and with a compatible business model across international borders and technology.
India’s Global Partnerships with Cross-Border Payment Networks
A clear example of an interoperable cross-border payments partnership is that between India’s UPI and Singapore’s PayNow. The need for faster cross-border payments and financial inclusion has been a catalyst in establishing the link between India and Singapore. The interoperable link between UPI and PayNow, enables instantaneous, cost-effective, and transparent payments across borders.
Now for those new to UPI, it is India’s real-time payment system with a Virtual Payment Address (VPA). It is completely mobile-based and supports person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) payments and funds transfers.
And PayNow is Singapore’s real-time payment system available to all participating banks and non-bank financial institutions. It is also a mobile-based system and enables peer-to-peer funds transfer using mobile numbers, VPA, or Singapore NRIC/ FIN. The UPI-PayNow partnership is only the beginning and is established to foster faster and smoother transactions between India and Singapore.
India also holds strategic partnerships with the following payments networks and banks to enable seamless, interoperable international transactions.
- Discover Financial Services (DFS), US
- Japan Credit Bureau (JCB), Japan
- Union Pay International (UPI), China
- Royal Monetary Authority (RMA), Bhutan
- Mashreq Bank, UAE
- Lycra Network, France (in the pipeline)
Benefits of Payments Interoperability
Interoperability benefits the entire payment ecosystem, including customers, merchants, end-users, and businesses. In addition to enhancing user experience and helping mitigate security risks, it delivers the advantages below.
- Payment flexibility: The ability to accept all forms of payments is a game-changer. Universal payment acceptance helps customer retention and increases customer reach. Though there are several digital payment systems and digital offerings from payment system providers, customers are not required to sign into multiple systems and complete their KYC many times. Interoperability brings issuers and acquirers together to undertake, clear, and settle payment transactions across payment systems, ensuring universal payments and consumer retention.
- Faster payment system: Electronic transactions are the key to reconciling and collecting payments, unlike cash-based systems. Advanced technology and fast internet connectivity make it easier to increase the speed of transactions.
- Secure payment and POS integration: Integration pushes the transaction directly to the payment terminal and eliminates manual entries, thereby enhancing security.
- Low operational costs: Integrated payment platforms reduce operating costs and seamlessly communicate with multiple devices across different financial service providers. It helps save money on adding new payment terminals.
Addressing Challenges — Getting it Right
Getting interoperability right through open API- based platforms is a start toward harnessing and expanding the payments ecosystem. Interoperability can be tricky when dealing with legacy systems. Technical challenges usually comprise systems that use different technical standards, communication protocols, and related software and hardware infrastructure. Another common challenge relates to data and semantics. Payment systems may use different languages and need to be translated. Inadequate translation leads to corrupted or lost data.
It is crucial to address the regulatory, technical, and business challenges of interoperability to make cross-border payments affordable, faster, transparent, and inclusive. Strategic partnerships with fintech firms, banks, exchange houses, and Money Transfer Operators (MTOs) with a focus on regulatory compliance and technology innovation will pave the way to overcome challenges and enable frictionless international transactions.
Need of the Hour for Today’s Generation
Payments interoperability is the linchpin of today’s digitized economy. When done right, it can lead to greater convenience, speed, reliability, security, and seamlessness. It is the need of the hour today, as it enables people from all walks of life to benefit from the convenience that the cashless economy offers. It can increase service offerings, reduce costs, empower the end-user and help improve payment systems. Thus, interoperability is a strong facilitator for financial inclusion.
By leveraging API-based cross-border payment platforms with simple integrations across domestic switches, bank accounts, mobile wallets/e-wallets, MTO transfers, and forex card solutions, we can enable financial inclusion and seamless payments across APAC and MENA regions. With India to start with and then extended globally.
Along these lines, M2P is proud to partner with LivQuik for UPI services on exiting PPI offerings like cards, wallets, gift certificates, and other products. Thereby enabling interoperable payments on the LivQuik platform.
Want to know more about building interoperable payment systems?
Write to us at [email protected].
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the latest fintech news, views, and insights, directly to your inbox.
Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for insightful fintech tales curated for curious minds like you.
Why Payments Interoperability is a Must for Today’s Generation? was originally published in M2P Fintech on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
